- Pressure (what it is and units)
- Temperature (Use Kelvin Scale, 273.15)
- Volume conversions
| Pa | (N/m2) | 101325 Pa = 1 atm |
| bar | (105 Pa) | 1.01325 bar = 1 atm |
| torr and mmHg | (133.322 Pa) | 760 torr = 1 atm |
| atmosphere | (101325 Pa) | |
| PSI | (6894.76 Pa) | 14.7 PSI = 1 atm |
| Unit | Liter | m3 |
| m3 | 10-3 | 1 |
| cm3 (ml) | 103 | 106 |
| liter (dm3) | 1 | 103 |
| ft3 | 0.02831 | 28.31 |
| in3 | 1.639 x 10-5 | 0.01639 |
- No volume
- No interaction
- Discuss behavior of ideal gas
- 1 bar (105 Pa), previously 1 atm
- 0 °C
- Derive relationship from ideal gas concept with picture on board
- Animation from CD-ROM ( d:, e:, f:, g:, h:, Mac )
- Graph relationship
- Write equation for graph
- Work a problem. Given an initial volume of 350 in3 and a compression ratio of 10:1, what is the final volume?
- Derive relationship from ideal gas concept with picture on board
- Animation from CD-ROM ( d:, e:, f:, g:, h:, Mac )
- Graph relationship
- Write equation for graph
- Work a problem. A pressure cooker starts out at 25 C and 1 atm pressure. What is the pressure at 200 C?
- Derive relationship from ideal gas concept with picture on board
- Graph relationship
- Write equation for graph
- Work a problem. 1 m3 of steam is heated from 100 C to 500 C at constant pressure. What is the final volume?
- Derive relationship from ideal gas concept with picture on board
- Animation from CD-ROM ( d:, e:, f:, g:, h:, Mac )
- Graph relationship
- Write equation for graph
- Work a problem.
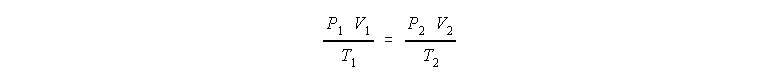
- A stratospheric sampling balloon starts at sea level, 760 torr and 20 C with a volume of 1000 m3. The balloon rises to a pressure altitude of 1000 Pa (appx 40 km) where the temperature is -40 C. What is the volume of the balloon at this altitude?
- Gas data for 1 gram at STP. Calculate the molar volume
- H2 11.1 L
- He 5.57 L
- N2 0.800 L
- Cl2 0.316 L